
Evgenii S Stoyanov
Russian Academy of Sciences, Russia
Title: Dialkyl halonium ions, R2X+ (X = F, Cl): Stability and chemical properties
Biography
Biography: Evgenii S Stoyanov
Abstract
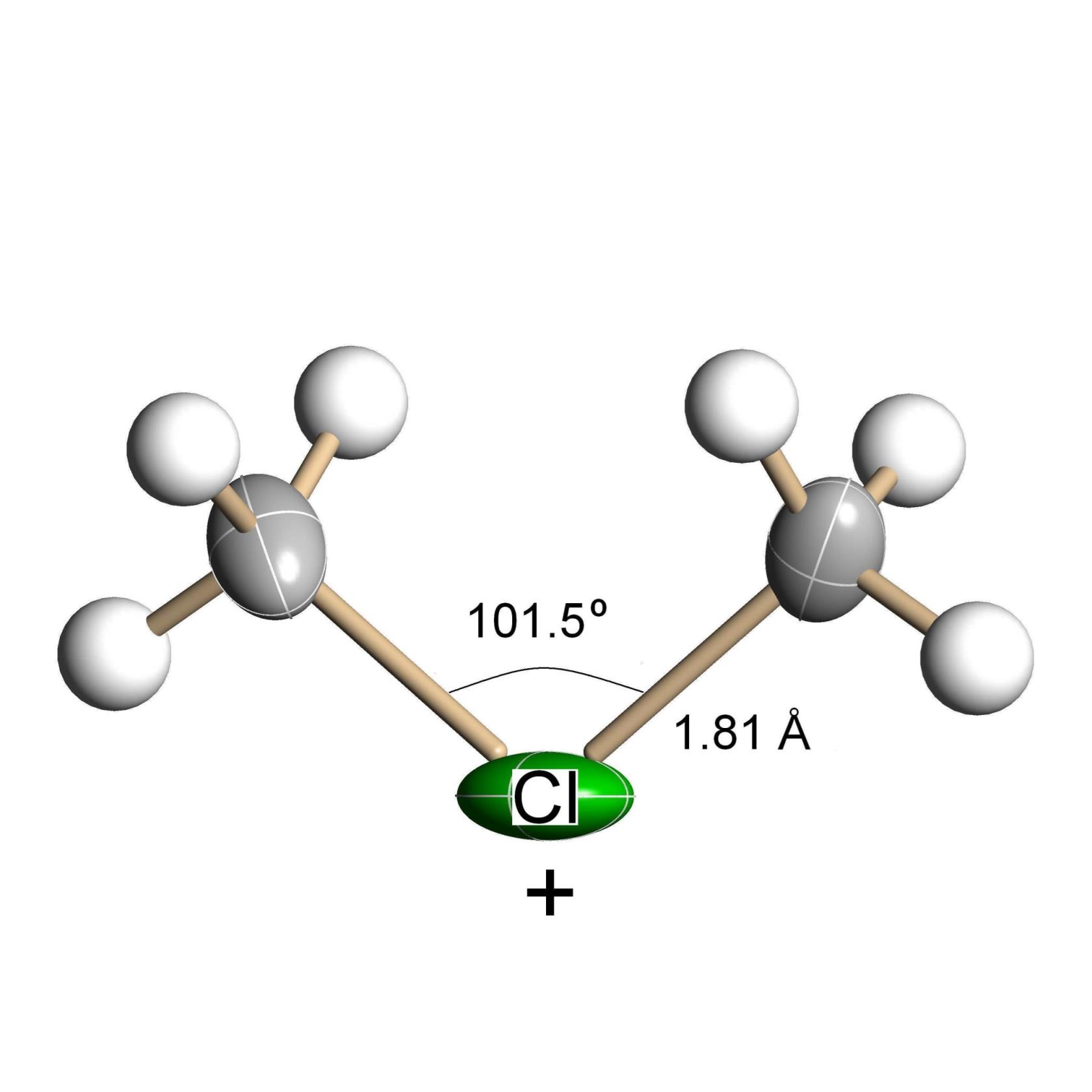
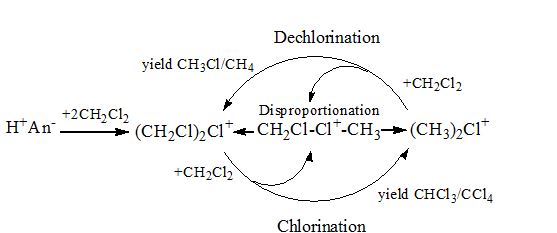
Halonium ions (R2Hal+) are reactive intermediates in electrophilic chemistry and are effective methylating and protonating agents for a variety of compounds. Chloronium cations (Figure 1) in their salts (CnH2n+1)2Cl+(CHB11Cl11−), at n=1 to 3 and with exceptionally stable carborane anions, are stable at ambient and elevated temperatures. Their temperature of decomposition decreases with the n increasing from 1 (ca. 150oC) to 3 (ca. 80oC) because of increasing ionicity of C-Cl bonds in the C-Cl+-C bridge. At room temperature, the salts of cations at n≥4 are unstable and decompose. It was shown indirectly that the unstable salt of fluoronium ions (CH3)2F+(CHB11F11−) must exist at low temperatures. The proposed (CH3)2F+ cation is much more reactive than the corresponding chloronium, showing at room temperature the chemical properties expected of chloronium at elevated temperatures. (CH3)2F+ and CH3F+C2H5 are decomposed yielding cations C2H5 + or C3H7 + respectively. Interaction of chloronium cations with chloroalkanes was studied here; for example, interaction of (CH3)2Cl+ with CH3Cl at 160oC results in formation of the tert-Bu+ cation. Interactions of the salts of chloronium ions, R-Cl+-R (R=CH3, CH2Cl), with gaseous and liquid di-chloromethane have been studied. In liquid CH2Cl2, they act as catalysts converting CH2Cl2 to CHCl3/ CCl4 (chlorination) or to CH3Cl/CH4 (dechlorination). The mechanism of the catalytic processes was determined.
References:
- Stoyanov E (2017) Chemical Properties of Dialkyl Halonium Ions (R2Hal+) and Their Neutral Analogues, Methyl Carboranes, CH3− (CHB11Hal11), Where Hal = F, Cl. J. Phys. Chem. A, 121:2918-2923.
- Stoyanov E (2016) The salts of chloronium ions R–Cl+–R (R = CH3 or CH2Cl): formation, thermal stability, and interaction with chloromethanes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 18:4871-4880.
- Stoyanov E., Stoyanova I., Tham F., Reed C. (2010) Dialkyl Chloronium Ions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132:4062-4063.
- Stoyanov E., Stoyanova I., Reed C. (2011) Oligomeric Carbocation-like Species from Protonation of Chloroalkanes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133:8452-8454.

